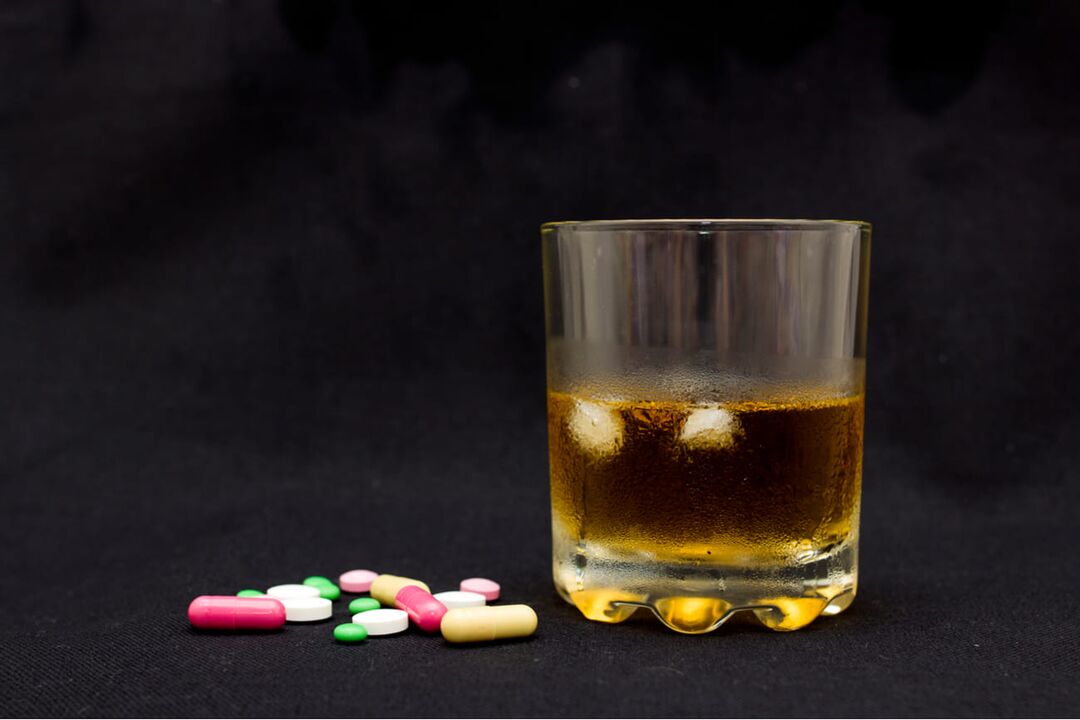
Almost each of us has faced diseases that require the use of antibacterial drugs to achieve a therapeutic effect. They are aggressive drugs towards the microflora. That is why the question arises of how soon one can drink alcohol after antibiotics, since many would not want to give up wine, cognac, beer or vodka for a long time.
The question is ambiguous and there is no direct monosyllabic answer. There are different opinions in the media. Some people, during a holiday with a party, believe it is more correct to refuse to drink alcoholic beverages, relying more on intuition than on reliable information from authoritative sources. Such a person in a company evokes sympathy and understanding, usually nonehe doesn't convince him to drink. However, there are times when someone refers to an article where a doctor commonly explains what does not always interfere with the healing process.
Why you shouldn't take medications with alcohol
As you know, there is no smoke without fire. Doctors can scientifically justify banning the use of antimicrobial agents while simultaneously consuming vodka or beer. In addition, they claim that it is possible to take antibiotics after drinking alcohol after a strictly defined period of time. Experts appeal to the following facts:
- ethanol at the biochemical level significantly reduces the therapeutic effect of antimicrobial agents;
- the combination of alcohol and antibacterial drugs causes toxic damage to liver cells and other internal organs;
- Alcohol consumption suppresses the immune system and has a devastating effect on health, which during the period of drug therapyhighly undesirable.
There is a rational streak in the above arguments. The biochemical processes occurring in the body are extremely complex and balanced, so saturation of the tissues of internal organs with a biologically active compound such as ethyl alcohol cannot but affect the metabolism. Alcohol can in fact significantly reduce the therapeutic effect of drugs. It destroys the atomic structure of the active ingredient or prevents the reaction of drugs with proteins of pathogenic microorganisms. Additionally, alcohol can speed up the elimination or make it difficult to absorb medications. This is how it happensdecrease in the effectiveness of therapyor you develop unwanted side symptoms.
Effect on liver function and condition
Scientific research and practice of clinical medicine confirm the destructive effect on the liver of the combination of antimicrobial drugs with alcoholic beverages. That is why the instructions for use of the drugs indicate contraindications and side effects on this extremely important organ. For patients with chronic liver disease, many drugs are unavailable. If you combine antimicrobial drugs and alcohol, the negative impact will be double. How soon should you drink alcohol after a course of antibiotics?It depends on the general conditionsthe body and its ability to recover.
Under the action of enzymes, ethanol is broken down into water and carbon dioxide, but not immediately, but bypassing the intermediate stage of the formation of an extremely toxic compound - acetaldehyde, which is a tissue poison. The faster alcohol breaks down, the less damage it causes to the body. However, with the simultaneous presence of antimicrobial drugs in the tissues of internal organs, the catabolism of alcohol slows down significantly due to the inhibition of the production of the enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase, which is necessary to complete the reaction of degradation of ethanol into simple compounds.
Ethanol does not interact directly with antibiotics
To find out how alcohol affects medications and how many days you can drink alcohol after finishing a course of antibiotics,laboratory experience. First, scientists conducted experiments on animals, then invited volunteers who were asked to undergo a therapeutic course using antibacterial drugs. The participants were divided evenly into two groups. Representatives of the first group were offered alcoholic drinks during the experiment, while the second was not. The main goal that the organizers tried to achieve was to establish the effect of ethanol on the biological activity of drugs.
The results of the experiment showed that most antibacterial drugs interacted slightly or not at all with ethyl alcohol: it practically did not reduce the effectiveness of the drugs used. A similar conclusion was reached after studying and comparing the results of antibacterial drug therapy between the two groups. They turned out to be identical. The difference did not exceed the allowable error. The rate of absorption, distribution in the tissues of internal organs and also removal of the active ingredients wasapproximately the same.
HoweverOne should not make hasty conclusions about whether the simultaneous use of antibiotics and alcohol is completely safe. Experts ask you to take into account some nuances:
- the experiment was isolated and not confirmed by other studies, so one should not insist on the safety of the combination of drugs and alcohol;
- the experimental subjects were offered small doses of alcoholic beverages, but in real life moderation in the consumption of vodka and beer is quite rare;
- The studies concerned only the interaction of drugs with ethanol, the effect of this combination on the state of internal organs has not been studied, so the negative effect cannot be denied.
This was the first step towards a complete answer to the important question: how long after a course of antibiotics can you drink alcohol?no clear results.
Reasons to avoid drinking during treatment
Clinical medicine has every right to say that the combination of alcohol and drugs should be avoided. Although their effects on each other have not been adequately studied, enough is known about the health effects of ethanol to make any firm conclusions. It is impossible to deny that:
- alcohol disrupts metabolic processes if drunk regularly;
- ethanol causes an increase in blood sugar levels;
- alcohol consumption leads to physical and nervous exhaustion;
- the risk of an allergic reaction increases by an order of magnitude.
Each person has individual characteristics of internal biological processes, so it is possible to predict the body's reactionalmost impossible, but it is unlikely to be positive.
Interaction of alcohol with antimicrobial drugs
According to the experiment, consumption of alcohol-containing beverages does not affect the pharmacological properties of most antimicrobial agents and does not cause significant side effects. However, there are antimicrobial drugs that absolutely cannot be taken with alcoholic beverages, because such a combination leads to truly dangerous consequences.
Just a few days laterYou can drink alcohol after taking antibiotics, which affect your metabolism. For example, such drugs against fungal infections and their analogues require the participation of an enzyme in the biochemical reaction also necessary for the degradation of ethanol. Its supplies are limited. When significant doses of ethanol are consumed, a conflict arises. There is simply not enough enzyme to interact with the drug or to react with the ethyl alcohol. In the first case we will certainly observe a decrease in the therapeutic effectiveness of the drug, as well as possible allergic reactions and an increase in the side effects of the drug. If ethanol is not broken down, acute intoxication with all the resulting consequences cannot be avoided. That is why you should not take antimicrobial agents of this type at the same time as alcohol.
A disulfiram-like reaction is the main reason for prohibiting alcohol consumption during antimicrobial therapy. Interfering with the catabolism of ethanol in the body leads to the accumulation of the aforementioned acetaldehyde - acetaldehyde. This is a powerful toxin that has an overall negative effect on the body. The most common andunpleasant signs of intoxication:
- nausea with attacks of vomiting;
- stomach ache;
- acute headache;
- profuse sweating;
- general weakness, dizziness;
- tachycardia;
- increase in pressure.
I agree that this physical condition clearly demonstrates the point that antibiotics should be used after a course of alcohol a few days later, so that ethanol and its toxic breakdown products have time to leave the body naturally.
By the way, the disulfiram-like reaction is so called because of the drug for prohibitive drug therapy for chronic alcoholism: disulfiram. Its use forces alcoholics to stop drinking alcohol precisely because of the development of panic fear of symptomsacute intoxication. The drug is injected into the subcutaneous (implanted) layer, from where it gradually enters the body and blocks the production of the enzyme responsible for the breakdown of ethanol.
What complications to expect
The time it takes to safely drink alcohol again after a course of antibiotics depends on the antimicrobial drug (the speed of its absorption and elimination), as well as the individual characteristics of a person's metabolism.
Doctors emphasize that the ban does not apply only to a glass of cognac or vodka. You have to forget about wine, beer and soft drinks. Furthermore, ethyl alcohol is often found in other foods, as well as in medicines, so you need to pay attention to this aspect.
You can often hear that someone you know has been drinking alcohol and taking antimicrobial drugs, without any negative consequences. However, no one knows what happened to this man's body,how effectiveIt turned out that the treatment lasted, how long it lasted, how is his health now. Meanwhile, in the practice of clinical medicine, many cases were recorded when people did not adhere to the recommendation on how long to drink alcohol after antibiotics, but drank it during treatment and ultimately became its victims:
- violationsliver function;
- anaphylactic shock;
- disruptions in the functioning of the brain and the central nervous system in general (severe headache accompanied by dizziness, nausea with attacks of vomiting, convulsive attacks);
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- sleep dysfunctions;
- hypertension;
- negative skin reactions (dermatitis);
- heart rhythm disorders;
Our natural filter, the liver, is the one that suffers the most. Despite the ability to renew cells, it is affected so negatively that it eventually loses functionality.
The final word in the debate over combining alcohol and antibiotics
After completing drug therapy you need to wait a few days before starting to drink alcohol. This is due to the removal of the products of drug catabolism from the body, and this requires a certain period of time. All drugs have different times to reach maximum concentrations in the blood and be eliminated. Is alwaysindicated in the instructions.
It is not recommended to consume alcoholic beverages simultaneously not only with antimicrobial agents, but also with other drugs. However, antimicrobial drugs are one of the few that are strictly prohibited. If you plan to undergo a course of drug treatment, be sure to ask your doctor how long you can drink alcohol after taking antibiotics.
Despite the fact that expert opinion on the admissibility of the simultaneous use of alcoholic beverages and antibacterial drugs is divided (excluding those drugs that havethe restrictions are clear), most doctors are inclined to conclude that it is best for patients to stop drinking alcohol during treatment.
In any case, alcoholic beverages are not a product worth risking your health for, even if the risk seems insignificant. Nothing bad will happen if you become an avid teetotaler for 2 weeks. Even a healthy person's body succumbs to alcohol over time. Long-term consumption of alcoholic beverages leads to the development of a large number of different somatic and mental disorders. If a person does not give up alcohol during illness, then we can confidently say that it is physical and mentaldegradation will accelerateduring this period of time. Even if you could drink alcohol while taking medications, you still shouldn't. Ethanol is a poison, but it is impossible to count how many fates vodka has broken